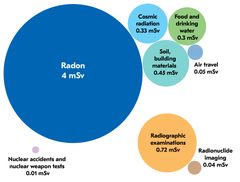
Radon causes most of the radiation received by Finns

The average effective radiation dose received by Finns is 5.9 millisieverts (mSv). Two-thirds of the radiation dose, 4 mSv, comes from indoor air radon. About 1.1 mSv is caused by other types of radiation than natural background radiation from indoor air radon. Background radiation is partly cosmic radiation from space and partly the radiation from radioactive materials in soil and building materials.
On average, the medical use of radiation causes a Finnish person an annual effective dose of 0.76 mSv. The radiation dose caused by radioactive materials in Finnish nature following nuclear accidents and nuclear weapon experiments that were carried out in the 1960s is very small.
The effective dose describing exposure to ionizing radiation is a calculated quantity that describes the detriment caused by radiation on a person’s health. As the effective dose grows, so does the risk of contracting cancer caused by radiation.
The last time STUK published calculations about the average radiation doses received by Finns was in 2012. The new numbers are different from the previous ones. For example, the use of radiation in medical examinations has grown a little, mostly due to the increase in the number of performed CT scans. Some of the changes in the numbers is caused by the new way of calculating effective doses.
New way of calculating radiation dose caused by radon
The biggest change compared to the 2012 calculations has to do with the effective dose caused by radon. The method used in the new calculations is the International Commission on Radiological Protection’s (ICRP) calculation method, published in 2017. Due to the new method, the effective dose caused by radon is more than twice of that compared to the last estimation.
Even though the risk of contracting cancer grows with the effective radiation dose, the average amounts of effective doses from different sources do not directly describe the risk. According to Teemu Siiskonen, the Deputy Director of STUK, the health risk caused by radon is estimated on the basis of epidemiologic examinations, not the effective dose. This means that the number of cases of lung cancer caused by radon does not change despite the new calculation method. Every year, an average of 280 Finns die from lung cancer caused by radon. Of these cases, 240 deaths are induced by smoking in addition to radon.
Link to the publication (in Finnish)
Further information:
Deputy Director Teemu Siiskonen, tel. +358 (0)9 759 88 318
Media contacts, tel. +358 10 850 4761
Images
About Säteilyturvakeskus (STUK)
Säteilyturvakeskus (STUK) on sosiaali- ja terveysministeriön hallinnonalan viranomainen, joka valvoo säteily- ja ydinturvallisuutta Suomessa. Tehtävämme on ihmisten, yhteiskunnan, ympäristön ja tulevien sukupolvien suojelu säteilyn haitallisilta vaikutuksilta.
Subscribe to releases from Säteilyturvakeskus (STUK)
Subscribe to all the latest releases from Säteilyturvakeskus (STUK) by registering your e-mail address below. You can unsubscribe at any time.
Latest releases from Säteilyturvakeskus (STUK)
STUK:s luftinsamlare fångade radioaktivt brom18.12.2025 11:12:26 EET | Pressmeddelande
Strålsäkerhetscentralen upptäckte en ofarlig liten mängd radioaktivt brom i utomhusluften i Vanda i ett prov som samlades in den 11-12 december. Brom kan härstamma till exempel från en spårämnesmätning som har utförts korrekt i en industrifacilitet, där en radioaktiv isotop av brom har använts som spårämne.
STUKin ilmankerääjään tarttui radioaktiivsta bromia18.12.2025 11:12:26 EET | Tiedote
Säteilyturvakeskus havaitsi Vantaan ulkoilmassa haitattoman pienen määrän radioaktiivista bromia joulukuun 11.-12. kerätyssä näytteessä. Bromi voi olla peräisin esimerkiksi teollisuuslaitoksessa asiallisesti tehdystä kokeesta, jossa bromin radioaktiivista isotooppia on käytetty merkkiaineena.
Radonhalten i hemmet kan inte fastställas utifrån grannbostadens mätresultat15.12.2025 11:32:26 EET | Pressmeddelande
Enligt en utredning av Strålsäkerhetscentralen kan radonhalterna variera betydligt i samma husbolags bostäder. Radonhalten är inte konstant ens i en enskild bostad. Radonbekämpningen i byggskedet av nya hus och radonsaneringen i ett senare skede fungerar länge, men uppföljningen är viktig.
Kodin radonpitoisuutta ei voi päätellä naapuriasunnon mittaustuloksesta15.12.2025 11:32:26 EET | Tiedote
Säteilyturvakeskuksen selvityksen mukaan radonpitoisuudet voivat vaihdella saman taloyhtiön asunnoissa merkittävästi. Radonpitoisuus ei ole vakio edes yksittäisessä asunnossa. Uusien talojen rakennusvaiheen radontorjunta sekä myöhemmän vaiheen radonkorjaukset toimivat pitkään, mutta seuranta on tärkeää.
You cannot conclude your home’s radon concentration from the results measured in the neighbouring dwelling15.12.2025 11:32:26 EET | Press release
According to a report by the Radiation and Nuclear Safety Authority, radon concentrations may vary significantly between the dwellings within the same housing company. Radon concentration does not remain constant even in an individual dwelling. Radon prevention in the construction phase of new houses and radon mitigation measures in later stages work for a long time, but monitoring is important.
In our pressroom you can read all our latest releases, find our press contacts, images, documents and other relevant information about us.
Visit our pressroom
